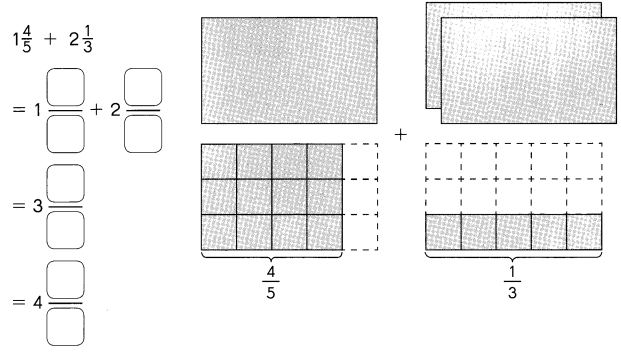
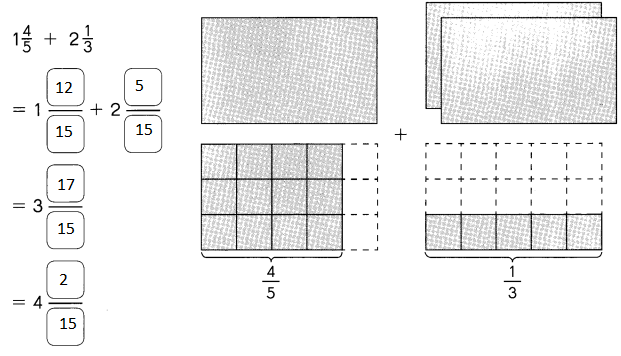
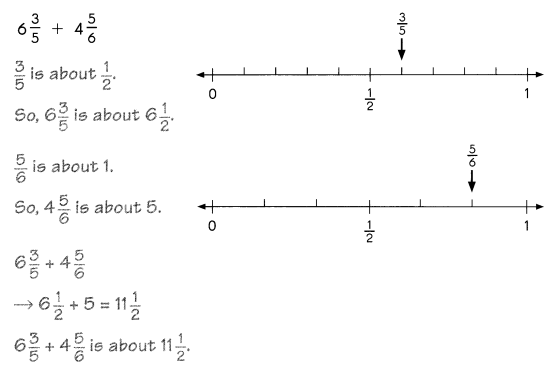
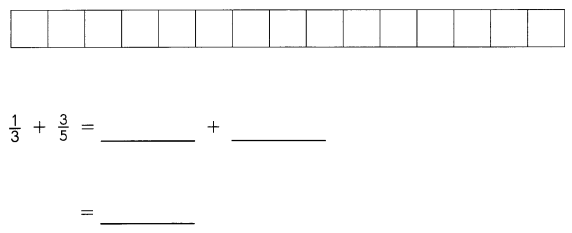
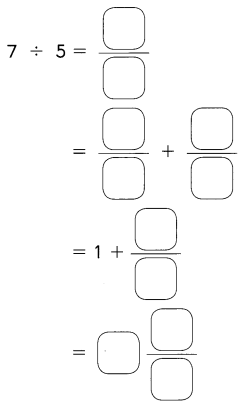
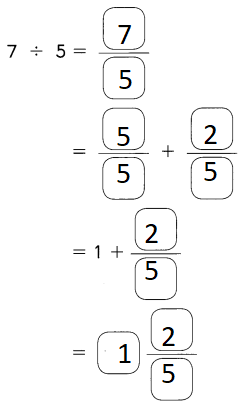
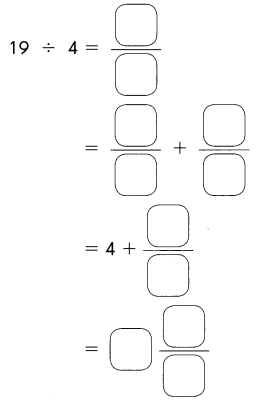
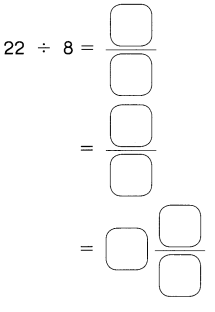
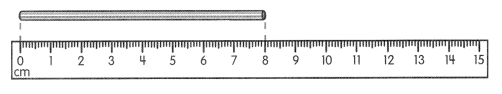
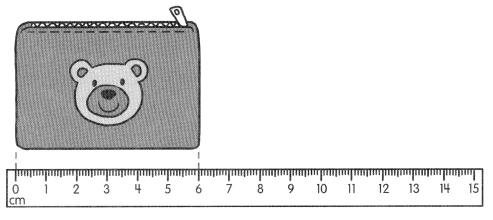
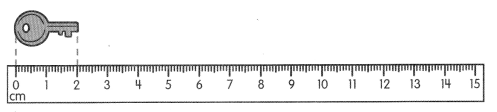
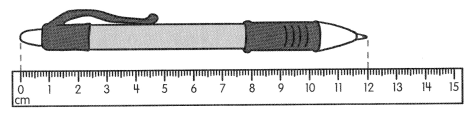
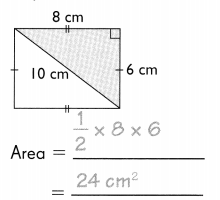
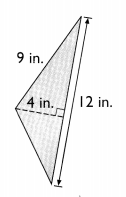
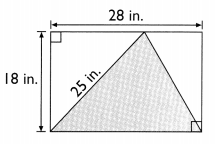
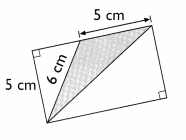
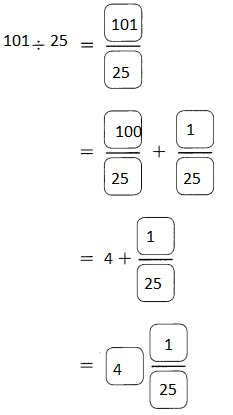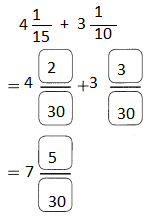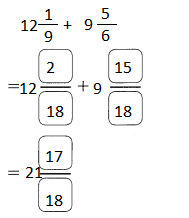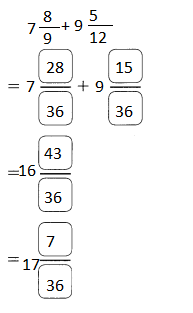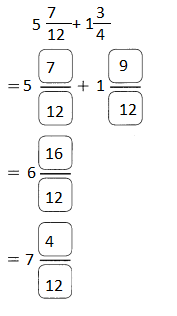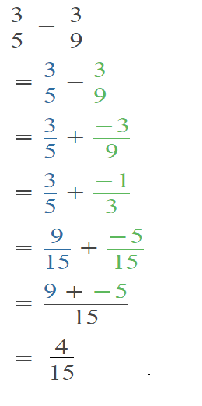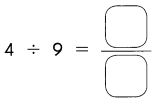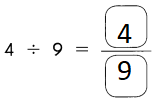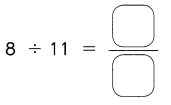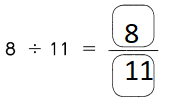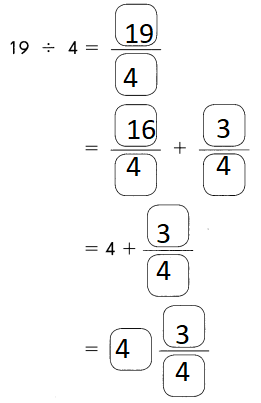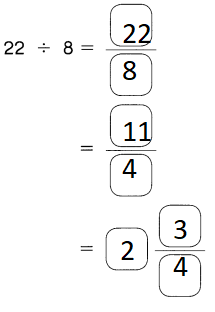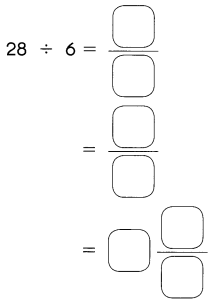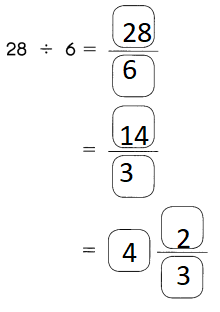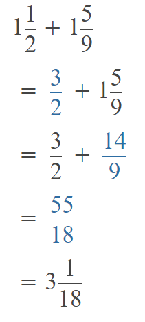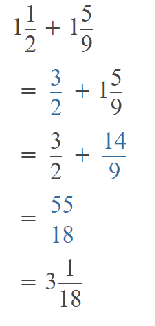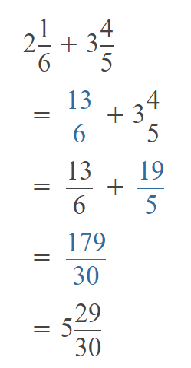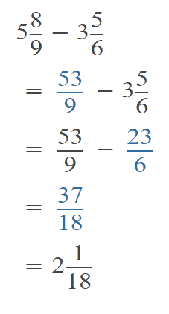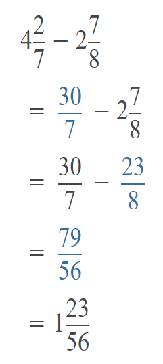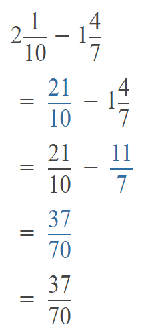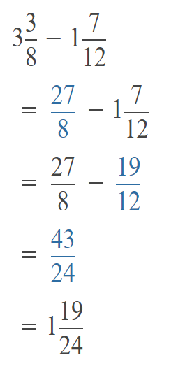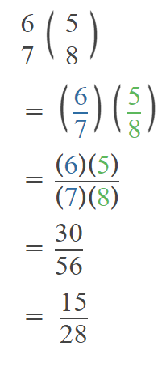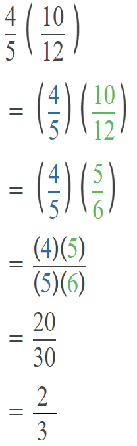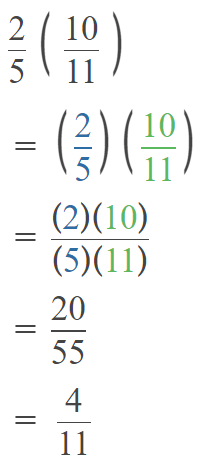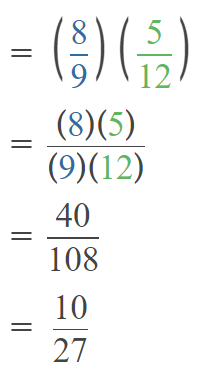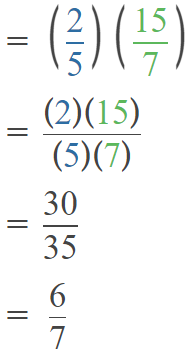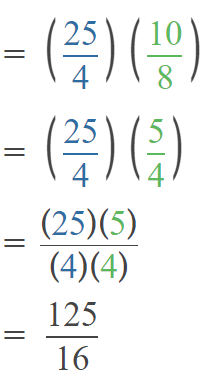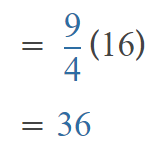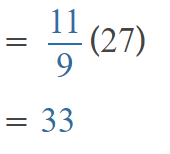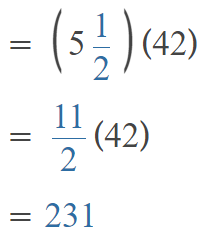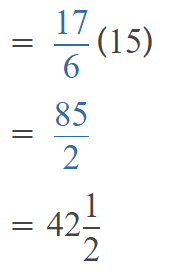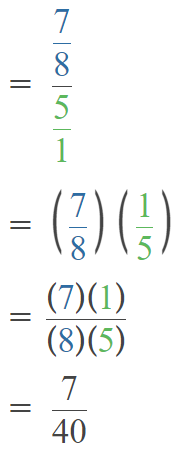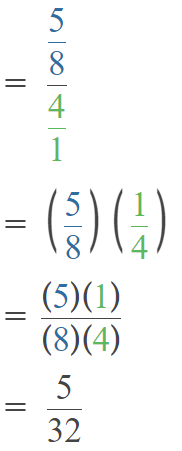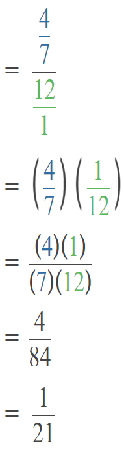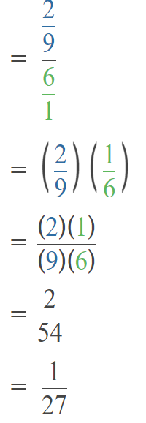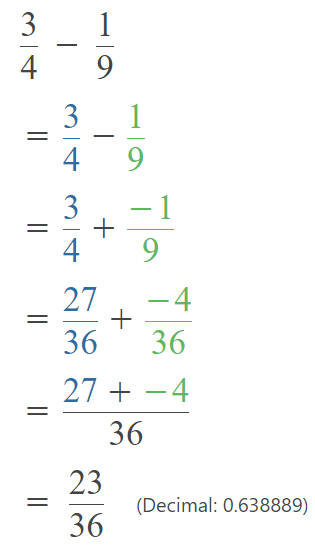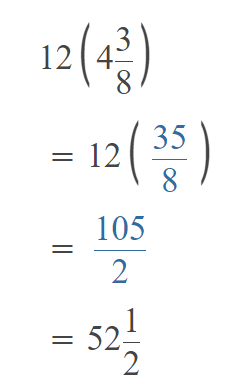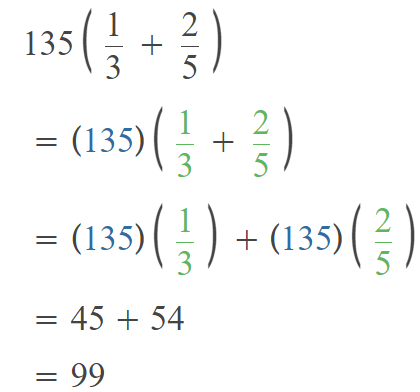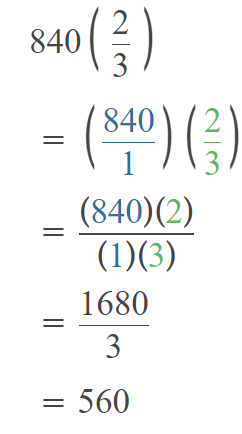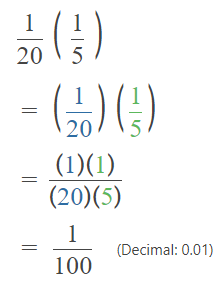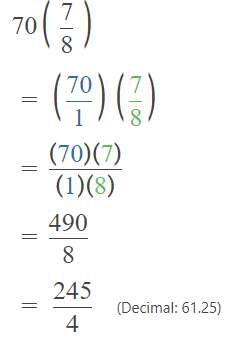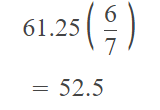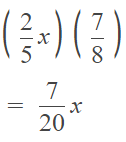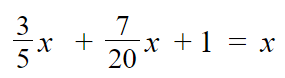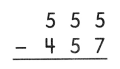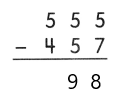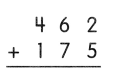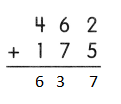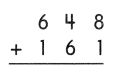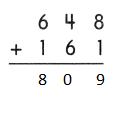Go through the Math in Focus Grade 5 Workbook Answer Key Chapter 1 Practice 5 Rounding and Estimating to finish your assignments.
Math in Focus Grade 5 Chapter 1 Practice 5 Answer Key Rounding and Estimating
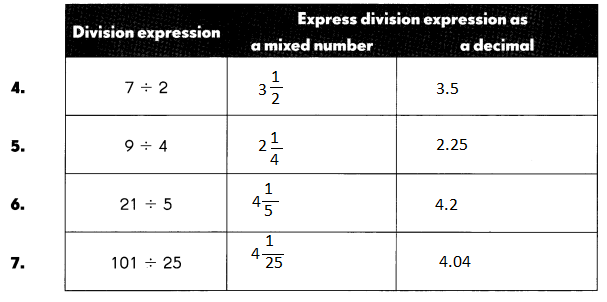
Mark an ✗ to show where each number is located on the number line. Then round each number.
Example
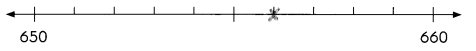
656 rounded to the nearest ten is 660
Question 1.
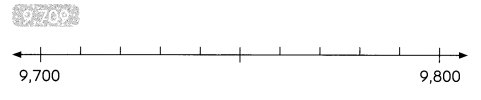
9,709 rounded to the nearest hundred is ____
Answer: 9,700
Rounding is a way of simplifying numbers to make them easier to understand or work with. Rounding can be used when an exact number isn’t needed, and an approximate answer will do.
When rounding a number such as 9709 to the nearest hundred, we use the following rules:
A) We round the number up to the nearest hundred if the last two digits in the number are 50 or above.
B) We round the number down to the nearest hundred if the last two digits in the number are 49 or below.
C) If the last two digits are 00, then we do not have to do any rounding, because it is already to the hundred.
In this case, Rule B applies and 9709 rounded to the nearest hundred is: 9,700
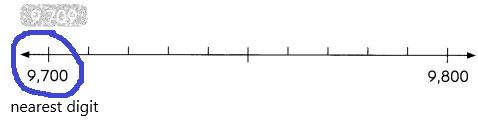
9,709 rounded to the nearest hundred is 9,700.
Question 2.
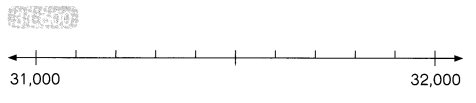
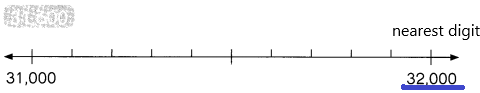
31,600 rounded to the nearest thousand is ___
Answer: 32,000
Rounding off the numbers means shortening the length of the number from long digits by replacing it with the nearest value. Round of to the nearest 1000 means minimizing the given decimal number to its nearest 1000 value.
How to round off the numbers to the nearest 1000:
Based on the below steps, we can easily round the numbers to the nearest 1000.
1. First, Find out the thousand’s digit in the number.
2. Next, choose the next smallest number (that is the hundredth digit of the number).
3. Now, check the hundred’s digit is either <5 (That means 0, 1, 2, 3, 4) or > = 5 (That is 5, 6, 7, 8, 9).
(i) If the digit is < 5, then the hundreds place is replaced with the digit ‘0’.
(ii) If the digit is > = 5, then the hundred’s digit is replaced with the digit ‘0’, and the thousand’s place digit is increased by 1 digit.
Number 31,600 Round to the Nearest 1000
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 1.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 0.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘0’ is <5, then we have to apply 3(i) conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’.
31,600 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 32,000.
Round each number to the nearest thousand.
Question 3.
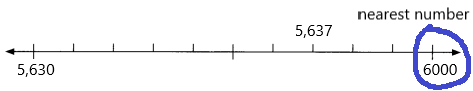
5,637 ____
Answer: 6000
Explanation:
Rounding off the numbers means shortening the length of the number from long digits by replacing it with the nearest value. Round of to the nearest 1000 means minimizing the given decimal number to its nearest 1000 value.
How to round off the numbers to the nearest 1000:
Based on the below steps, we can easily round the numbers to the nearest 1000.
1. First, Find out the thousand’s digit in the number.
2. Next, choose the next smallest number (that is the hundredth digit of the number).
3. Now, check the hundred’s digit is either <5 (That means 0, 1, 2, 3, 4) or > = 5 (That is 5, 6, 7, 8, 9).
(i) If the digit is < 5, then the hundreds place is replaced with the digit ‘0’.
(ii) If the digit is > = 5, then the hundred’s digit is replaced with the digit ‘0’, and the thousand’s place digit is increased by 1 digit.
Number 5,637 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 5.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 6.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘6’ is >5, then we have to apply 3(ii) conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’and the thousand’s place digit is increased by 1 digit.
5,637 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 6000.
Question 4.
9,541 ____
Answer: 10,000
Explanation:
Number 9,541 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 9.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 5.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘5’ is >=5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’and the thousand’s place digit is increased by 1 digit.
9,541 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 10,000.
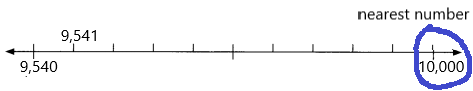
Question 5.
1,399 ___
Answer: 1000
Explanation:
Number 1,399 Round to the Nearest 1000
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 1.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 3.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘3’ is <5, then we have to apply conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’.
1,399 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 1000.
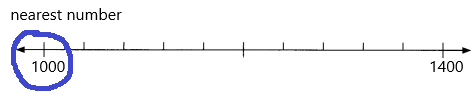
Question 6.
72,245 ____
Answer: 72000
Explanation:
Number 72,245 Round to the Nearest 1000
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 2.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 2.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘2’ is <5, then we have to apply conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’.
72,245 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 72,000.
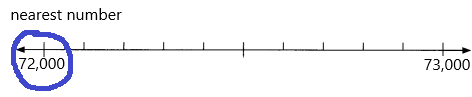
Question 7.
473,075 _________
Answer: 473,000
Explanation:
Number 473,075 Round to the Nearest 1000
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 3.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 0.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘0’ is <5, then we have to apply conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’.
473,075 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 473,000.
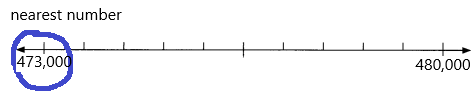
Question 8.
69,547 ___
Answer: 70,000
Explanation:
Number 69,547 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 9.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 5.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘5’ is >=5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’and the thousand’s place digit is increased by 1 digit.
69,547 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 70,000.
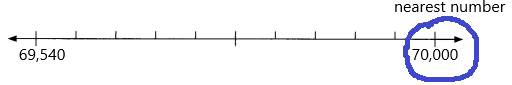
Question 9.
20,100 ____
Answer: 20,000
Explanation:
Number 20,100 Round to the Nearest 1000
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 0.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 1.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘1’ is <5, then we have to apply conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’.
20,100 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 20,000.
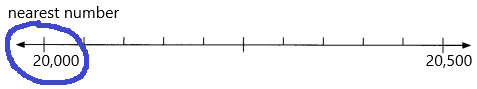
Question 10.
756,715 ____
Answer: 757000
Explanation:
Number 756,715 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 6.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 7.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘7’ is >=5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’and the thousand’s place digit is increased by 1 digit.
756,715 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 757,000.
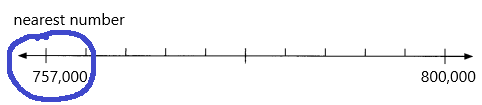
Answer each question. Use the number line to help you.
Example
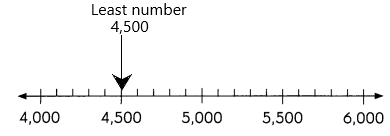
Rounding to the nearest thousand, what is the least and the greatest number that rounds to 3,000?
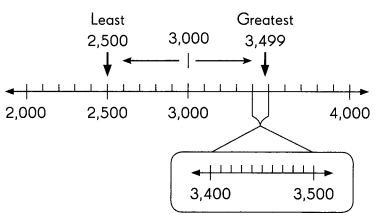
Least number: 2,500
Greatest number: 3,499
Question 11.
Rounding to the nearest thousand, what is
a. the least number that rounds to 5,000?

_______
Answer: The least number of 5000 is 4,500.
Explanation:
Number 4,500 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 4.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 5.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘5’ is >=5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’and the thousand’s place digit is increased by 1 digit.
4,500 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 5,000.
So, the least number to round up 5000 is 4,500.
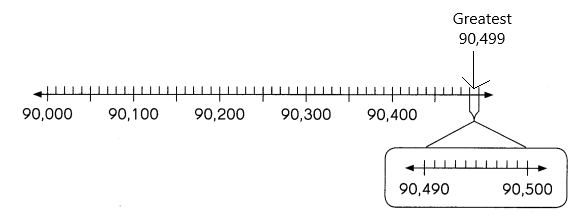
b. the greatest number that rounds to 90,000?
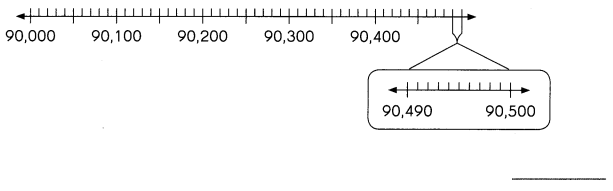
Answer:90,499
Explanation:
Number 90,000 Round to the Nearest 1000
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 0.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 0.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘0’ is <5, then we have to apply conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’.
But here the greatest number is asked to round up the 90,000 that means the number we need to find out to get the 90,000 if we calculate the nearest values to that number.
If I take 90,499.
Step 1: The thousand’s place is 0.
Step 2: Hundred’s place is 4.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘4’ is <5 then we have to apply conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’.
Finally, if we calculate 90,499 with the nearest 1000 with the above rules then the number will be 90,000.
Round each number to the nearest thousand. Then estimate the sum.
Example
9,286 + 5.703
9,286 rounds to 9,000.
5,703 rounds to 6,000.
9,000 + 6,000 = 15,000
Question 12.
6,789 + 4,200
Answer:11000.
Explanation:
Number 6,789 and 4,200 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 6 and 4.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 7 and 2.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘7’ is >=5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’and the thousand’s place digit is increased by 1 digit.
Step 4: The hundred’s digit ‘2’ is <5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’
6,789 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 7000.
4,200 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 4000.
Now add the rounded figures: 7000+4000=11000.
Question 13.
7,264 + 7,153
Answer:14000
Explanation:
Number 7,264 and 7,153 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 7 and 7.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 2 and 1.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘2’ is <5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’.
Step 4: The hundred’s digit ‘1’ is <5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’.
7,264 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 7000.
7,153 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 7000.
Now add the rounded figures: 7000+7000=14000.
Question 14.
4,885 + 6,075
Answer: 11000
Number 4,885 and 6,075 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 4 and 6.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 8 and 0.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘8’ is >=5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’ and the thousand’s place digit is increased by 1 digit.
Step 4: The hundred’s digit ‘1’ is <5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’.
4,885 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 5000.
6,075 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 6000.
Now add the rounded figures: 5000+6000=11000.
Question 15.
3,105 + 9,940
Answer: 13000
Number 3,105 and 9,940 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 3 and 9.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 1 and 9.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘9’ is >=5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’ and the thousand’s place digit is increased by 1 digit.
Step 4: The hundred’s digit ‘1’ is <5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’.
3,105 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 3000.
9,940 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 10000.
Now add the rounded figures: 3000+10000=13,000.
Question 16.
7,083 + 2,607
Answer:10,000
Number 3,105 and 9,940 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 7 and 2.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 0 and 6.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘0’ is <5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’.
Step 4: The hundred’s digit ‘6’ is >=5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’ and the thousand’s place digit is increased by 1 digit.
7,083 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 7000.
2,607 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 3000.
Now add the rounded figures: 7000+3000=10,000.
Round each number to the nearest thousand. Then estimate the difference
Example
8,156 – 6,109
8,156 rounds to 8,000.
6,109 rounds to 6,000.
8,000 – 6,00 = 2,000
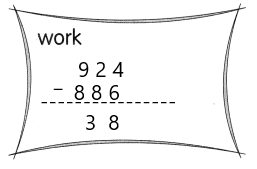
Question 17.
4,924 – 4,127
Answer: 1000
Number 4,924 and 4,127 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 4 and 4.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 9 and 1.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘1’ is <5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’.
Step 4: The hundred’s digit ‘9’ is >=5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’ and the thousand’s place digit is increased by 1 digit.
4,924 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 5000.
4,127 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 4000.
Now add the rounded figures: 5000-4000=1,000.
Question 18.
7,105 – 3,940
Answer:3000
Number 7,105 and 3,940 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 7 and 3.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 9 and 1.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘1’ is <5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’.
Step 4: The hundred’s digit ‘9’ is >=5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’ and the thousand’s place digit is increased by 1 digit.
7,105 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 7000.
3,940 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 4000.
Now add the rounded figures: 7000-4000=3000.
Question 19.
4,885 – 1,075 ____
Answer:4000.
Number 4,885 and 1,075 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 4 and 1.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 8 and 0.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘0’ is <5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’.
Step 4: The hundred’s digit ‘8’ is >=5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’ and the thousand’s place digit is increased by 1 digit.
4,885 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 5000.
1,075 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 4000.
Now add the rounded figures: 5000-4000=1000.
Question 20.
3,522 – 2,815
Answer:1000
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 3 and 2.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 5 and 8.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘8 and 5’ is >=5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’ and the thousand’s place digit is increased by 1 digit.
3,522 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 4000.
2,815 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 3000.
Now add the rounded figures: 4000-3000=1000.
Question 21.
6,480 – 1,397
Answer: 5000
Number 6,480 and 1,397 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 6 and 1.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 4 and 3.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘4 and 3’ is <5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’.
6,480 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 6000.
1,397 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 1000.
Now add the rounded figures: 6000-1000=5000.
Use front-end estimation with adjustment to estimate each sum.
Example
1,963 + 3,290 + 7,837
1,000 + 3,000 + 7,000
= 11,000
900 + 200 – &00
= 1,900
To the nearest thousanci:
1,900 → 2,000
11,000 + 2,000 = 13,000
Question 22.
2,541 + 6,061 + 1,681
Answer: 11000
With front end estimation, we only round and add the numbers in the leftmost place or the very last number on the left. This means that all numbers in other places will be zeros except the number in the leftmost place after the numbers are rounded. Having said that, if the numbers have two digits, round to the tens place before adding the leftmost digits or numbers.
Explanation:
Number 2,541, 6,061 and 1,681 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 2, 6, and 1.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 5, 0, and 6.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘0’ is <5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’.
Step 4: The hundred’s digit ‘5 and 6’ is >=5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’ and the thousand’s place digit is increased by 1 digit.
2,541 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 3000.
6,061 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 6000.
1,681 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 2000
The front end estimations are 3000, 6000, 2000.
Now add all those estimations:3000+6000+2000=11000.
Question 23.
7,823 + 6,848 + 3,310
Answer:
With front end estimation, we only round and add the numbers in the leftmost place or the very last number on the left. This means that all numbers in other places will be zeros except the number in the leftmost place after the numbers are rounded. Having said that, if the numbers have two digits, round to the tens place before adding the leftmost digits or numbers.
Explanation:
Number 7,823, 6,848 and 3,310 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 7, 6, and 3.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 8, 8, and 3.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘3’ is <5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’.
Step 4: The hundred’s digit ‘8 and 8’ is >=5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’ and the thousand’s place digit is increased by 1 digit.
7,823 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 8000.
6,848 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 7000.
3,310 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 3000
The front end estimations are 8000, 7000, 3000.
Now add all those estimations:8000+7000+3000=18000.
Question 24.
4,197 + 8,936 + 2,226
Answer:
With front end estimation, we only round and add the numbers in the leftmost place or the very last number on the left. This means that all numbers in other places will be zeros except the number in the leftmost place after the numbers are rounded. Having said that, if the numbers have two digits, round to the tens place before adding the leftmost digits or numbers.
Explanation:
Number 4,197, 8,936 and 2,226 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 4, 8, and 2.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 1, 9, and 2.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘1 and 2’ is <5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’.
Step 4: The hundred’s digit ‘9’ is >=5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’ and the thousand’s place digit is increased by 1 digit.
4,197 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 4000.
8,936 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 9000.
2,226 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 2000
The front end estimations are 4000, 9000, 2000.
Now add all those estimations:4000+9000+2000=15000.
Use front-end estimation with adjustment to estimate each difference.
Example .
2,943 – 1,272
2,000 – 1,000
= 1,000
900 – 200 = 700
To the nearest thousand:
700 → 1,000
1,000 + 1,000 = 2,000
Question 25.
6,770 – 3,081
Answer: 4000
Explanation:
With front end estimation, we only round and subtract the numbers in the leftmost place or the very last number on the left. This means that all numbers in other places will be zeros except the number in the leftmost place after the numbers are rounded. Having said that, if the numbers have two digits, round to the tens place before adding the leftmost digits or numbers.
Number 6,770 and 3,081 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 6 and 3.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 7 and 0.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘7 and 5’ is >=5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’ and the thousand’s place digit is increased by 1 digit.
Step 4: The hundred’s digit ‘0’ is <5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’.
6,770 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 7000.
3,081 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 3000.
The front end estimations are 7000, 3000.
Now add all those estimations:7000-3000=4000.
Question 26.
8,764 – 3,589
Answer: 5000
Explanation:
With front end estimation, we only round and subtract the numbers in the leftmost place or the very last number on the left. This means that all numbers in other places will be zeros except the number in the leftmost place after the numbers are rounded. Having said that, if the numbers have two digits, round to the tens place before adding the leftmost digits or numbers.
Number 8,764and 3,589 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 8 and 3.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 7 and 5.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘7 and 5’ is >=5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’ and the thousand’s place digit is increased by 1 digit.
8,764 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 9000.
3,589 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 4000.
The front end estimations are 9000, 4000.
Now subtract all those estimations:9000-4000=5000.
Question 27.
7,802 – 4,396
Answer: 4000
Explanation:
With front end estimation, we only round and subtract the numbers in the leftmost place or the very last number on the left. This means that all numbers in other places will be zeros except the number in the leftmost place after the numbers are rounded. Having said that, if the numbers have two digits, round to the tens place before adding the leftmost digits or numbers.
Number 7,802 and 4,396 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 7 and 4.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 8 and 3.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘8’ is >=5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’ and the thousand’s place digit is increased by 1 digit.
Step 4: The hundred’s digit ‘3’ is <5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’.
7,802 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 8000.
4,396 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 4000.
The front end estimations are 8000, 4000.
Now subtract all those estimations:8000-4000=4000.
Use front-end estimation with adjustment to estimate each difference.
Example
7,594 – 2,831
7,000 – 2,000 = 5,000
800 – 500 = 300
To the nearest thouari:
300 → 0
5,000 – 0 = 5,000
Question 28.
5,780 – 3,962
Answer: 2000
Explanation:
With front end estimation, we only round and subtract the numbers in the leftmost place or the very last number on the left. This means that all numbers in other places will be zeros except the number in the leftmost place after the numbers are rounded. Having said that, if the numbers have two digits, round to the tens place before adding the leftmost digits or numbers.
Number 5,780 and 3,962 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 5 and 3.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 7 and 9.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘7 and 9’ is >=5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’ and the thousand’s place digit is increased by 1 digit.
5,780 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 6000.
3,962 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 4000.
The front end estimations are 6000, 4000.
Now subtract all those estimations:6000-4000=2000.
Question 29.
9,119 – 4,852
Answer; 4000
Explanation:
With front end estimation, we only round and subtract the numbers in the leftmost place or the very last number on the left. This means that all numbers in other places will be zeros except the number in the leftmost place after the numbers are rounded. Having said that, if the numbers have two digits, round to the tens place before adding the leftmost digits or numbers.
Number 9,119 and 4,852 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 9 and 4.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 1 and 8.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘8’ is >=5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’ and the thousand’s place digit is increased by 1 digit.
Step 4: The hundred’s digit ‘1’ is <5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’.
9,119 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 9000.
4,852 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 5000.
The front end estimations are 9000, 5000.
Now subtract all those estimations:9000-5000=4000.
Question 30.
8,254 – 4,836
Answer: 3000
Explanation:
With front end estimation, we only round and subtract the numbers in the leftmost place or the very last number on the left. This means that all numbers in other places will be zeros except the number in the leftmost place after the numbers are rounded. Having said that, if the numbers have two digits, round to the tens place before adding the leftmost digits or numbers.
Number 8,254 and 4,836 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 8 and 4.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 2 and 8.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘8’ is >=5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’ and the thousand’s place digit is increased by 1 digit.
Step 4: The hundred’s digit ‘2’ is <5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’.
8,254 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 8000.
4,836 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 5000.
The front end estimations are 8000, 5000.
Now subtract all those estimations:8000-5000=3000.
Estimate each product.
Example
4,512 × 2
4,512 rounds to 5,000.
5,000 × 2 = 10,000
Question 31
3,765 × 7
Answer: 8000
Number 3,765 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 3.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 7.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘7’ is >=5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’ and the thousand’s place digit is increased by 1 digit.
3,765 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 4000.
The estimation is 4000
Now multiply with the given number that is 7:
4000×2=8000
Question 32.
2,521 × 5
Answer: 15000
Explanation:
Number 2,521 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 2.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 5.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘5’ is >=5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’ and the thousand’s place digit is increased by 1 digit.
2,521 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 3000.
The estimation is 3000
Now multiply with the given number that is 5:
3000×5=15000.
Question 33.
5,108 × 6
Answer: 30,000
Explanation:
Number 5,108 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 5.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 1.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘1’ is <5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’.
5,108 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 5000.
The estimation is 5000
Now multiply with the given number that is 6:
5000×6=30,000.
Question 34.
8,497 × 9
Answer: 72,000
Explanation:
Number 8,497 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 8.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 4.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘4’ is <5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’.
8,497 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 8000.
The estimation is 8000
Now multiply with the given number that is 9:
8000×9=72,000.
Question 35.
6,060 × 3
Answer:
Explanation:
Number 6,060 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 6.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 0.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘0’ is <5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’.
6,060 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 6000.
The estimation is 6000
Now multiply with the given number that is 3:
6000×3=18,000.
Estimate each quotient.
2,786 ÷ 5
2,500 ÷ 5
2,786 rounds to 3,000.
3,000 ÷ 5 = 600
Look for compatible numbers.
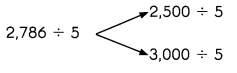
Which number is nearer to 2,786?
Question 36
6,509 ÷ 7
Answer: 1000
Explanation:
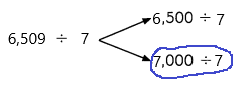
Why I choose 7000 to the nearest number I will explain below:
Number 6,509 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 6.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 5.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘5’ is >=5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’ and the thousand’s place digit is increased by 1 digit.
6,509 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 7000.
The estimation is 7000
Now divide with the given number that is 7:
7000÷7=1000.
Question 37.
5,512 ÷ 6
Answer: 1000
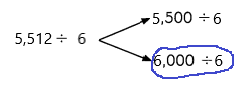
Explanation:
Why I choose 6000 to the nearest number I will explain below:
Number 5,512 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 5.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 5.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘5’ is >=5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’ and the thousand’s place digit is increased by 1 digit.
5,512 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 6000.
The estimation is 6000
Now divide with the given number that is 6:
6000÷6=1000.
Question 38.
2,785 ÷ 3
Answer: 1000
Explanation:
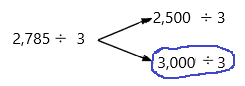
Number 2,785 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 2.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 7.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘7’ is >=5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’ and the thousand’s place digit is increased by 1 digit.
2,785 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 3000.
The estimation is 3000
Now divide with the given number that is 3:
3000÷3=1000.
Question 39.
6,287 ÷ 8
Answer: 750
Explanation:
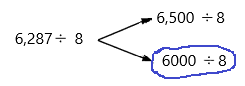
Number 6,287 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 6.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 2.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘2’ is <5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’.
6,287 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 6000.
The estimation is 6000
Now divide with the given number that is 8:
6000÷8=750.
Question 40.
2,963 ÷ 9
Answer: 333.33
Explanation:
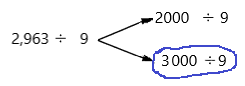
Number 2,963 Round to the Nearest 1000:
Step 1: Thousand’s digit of the number is 2.
Step 2: Hundred’s digit of the number is 9.
Step 3: The hundred’s digit ‘9’ is >=5, then we have to apply some conditions. That is, the hundred’s placed is replaced with the digit ‘0’ and the thousand’s place digit is increased by 1 digit.
2,963 rounding of the nearest 1000 is equal to 3000.
The estimation is 3000
Now divide with the given number that is 9:
3000÷9=333.33.